XSign in by: Email Mobile
星丰螺丝钉低碳钢平垫圈镀锌DIN125平垫圈平垫片
| Number | Unit-price | Total | |||
| I want to buy: | × | 0.01 | = | 0 |
A new item has been added to your Shopping Cart. You now have items in your Shopping Cart.
Related items
垫片(gasket)是两个物体之间的机械密封,通常用以防止两个物体之间受到压力、腐蚀、和管路自然地热胀冷缩泄漏。 由于机械加工表面不可能很好,使用垫片即可填补不规则性。 垫片通常由片状材料制成,如垫纸,橡胶,硅橡胶,金属,软木,毛毡,氯丁橡胶,丁腈橡胶,玻璃纤维或塑料聚合物(如聚四氟乙烯 )。 特定应用的垫片可能含有石棉。
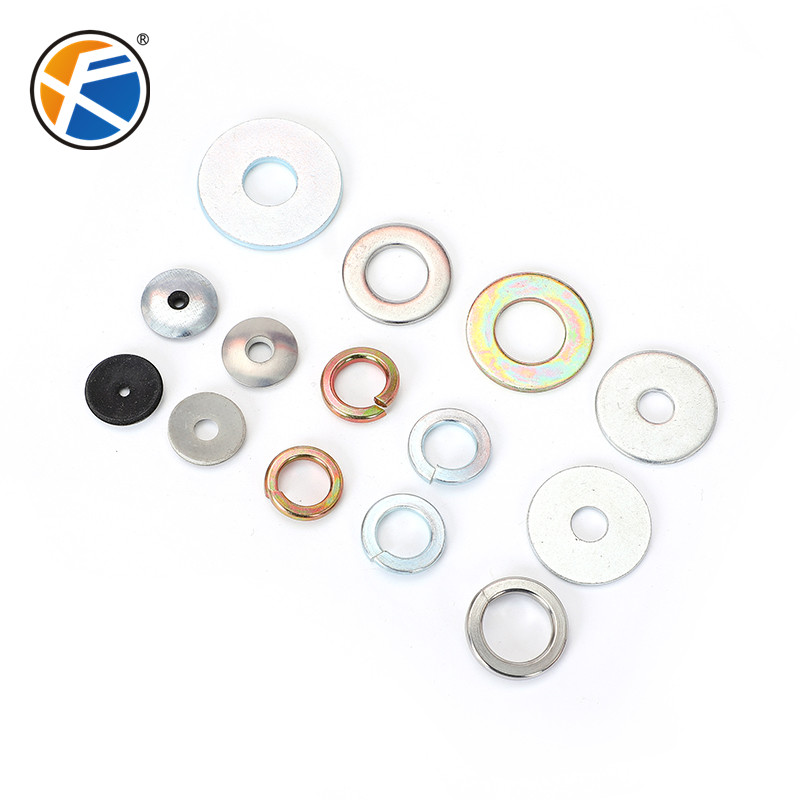
垫圈(washer)是薄板(通常圆型)的一个漏洞(通常在中间)通常是用于分配的负荷线程紧固件。其他用途是作为间隔,弹簧(贝尔维尔垫片,波垫片) ,耐磨垫,预显示装置,锁装置。 橡胶垫圈也用在水龙头(阀门)以切断流动的液体或气体。 橡胶或硅垫片也可使用,以减少风扇的振动。 通常垫片外径是内径的两倍左右 。
A gasket is a mechanical seal between two objects, usually used to prevent pressure, corrosion, and the natural expansion and contraction of pipes. Since machined surfaces can never be good, shim can be used to fill in irregularities. Spacers are usually made of sheet materials such as pad paper, rubber, silicone rubber, metal, cork, felt, neoprene, nitrile butadiene rubber, fiberglass or plastic polymers (such as teflon). Gaskets for specific applications may contain asbestos.
The washer is a leak (usually in the middle) of the sheet (usually round) usually used to distribute the load thread fasteners. Other uses are as spacers, springs (Belleville gaskets, wave gaskets), wear pads, pre-display devices, locking devices. Rubber washers are also used in faucets (valves) to cut off the flow of liquid or gas. Rubber or silicon shims may also be used to reduce fan vibration. Usually the outer diameter of the gasket is about twice the inner diameter.
Fold and edit this section type
Gaskets according to its material and structural characteristics can be divided into non-metallic gaskets, metal gaskets, metal-non-metallic combination of gaskets, and various types can be subdivided into several kinds.
Folding non-metallic gasket
Rubber gasket
Asbestos free fiber rubber gasket
Flexible graphite metal composite gasket
Teflon gasket
Teflon coated gasket
Other types of non-metallic material gaskets
gasket
gasket
Folding metal-nonmetallic composite gasket
Corrugated gasket
Metal wound gasket
Metal tooth compound gasket
Metal coated gasket
Metal wave tooth composite gasket
Other types of metal composite gaskets
Folding metal gasket
Metal flat gasket
Metal corrugated gasket
Metal toothed gasket
Metal ring gasket
Metal lens gasket
O-ring pad of metal
The metal ring gasket can be divided into
Octagonal ring pad
Elliptic ring pad
RX and BX type self-tightening ring pads
Fold and edit this section material classification
The part of the washer placed between the connector and the nut, usually a flat metal ring.
metallic gasket non-metallic gasket made of asbestos, rubber, synthetic resin, teflon and other nonmetallic metals. a non-metallic coated gasket Non-metallic jacket gasket outsourcing a layer of synthetic resin, etc.
semimetallic gasket A gasket made of metallic and nonmetallic materials, such as winding gasket, metal-coated gasket. a spiral wound gasket A gasket consisting of a metal belt with a V-shaped or W-shaped section and a non-metal belt. 1) The inner ring is a metal ring arranged in the inner ring of the winding gasket. 2) The outer ring is a metal ring arranged in the outer ring of the wound gasket. b Metal cladding
metallic gasket Metallic gasket made of metal such as steel, aluminum, copper, nickel, or monel.
Winding gasket refers to the metal belt (generally V-shaped steel belt) and non-metallic belt winding into a ring gasket, metal belt and non-metallic belt winding alternately, because of its good elasticity, widely used in the petrochemical, chemical, electric power and other industries of the flange seal structure, according to the specific position, can be in the inner or outer layer of the gasket with steel ring to locate or strengthen.
GB/T 4622.1-2009 Classification of winding gaskets
Gaskets for flanges of wound gaskets GB/T 4622.2-2008
GB/T 4622.3-2007 Technical specifications for winding gaskets
GB/T 9126-2008 Pipe flanges - Non-metallic flat gaskets - Dimensions
GB/T 9128-2003 Steel pipe flanges -- metallic ring gaskets -- Dimensions
Specification for non-metallic flat gaskets for pipe flanges
Specification for metal ring gaskets for GB/T 9130-2007 steel pipe flanges
Gaskets for large diameter steel pipe flanges
GB/T l3404-2008 Pipe flanges with non-metallic polytetrafluoron coated gaskets
Metal coated gaskets for pipe flanges
GB/T l9066.1-2008 Flexible graphite metal wave tooth composite gasket dimensions
GB/T l9066.3-2003 Flexible graphite metal wave tooth complex gaskets -- technical specifications
GB/T l9675.1-2005 Flexible graphite composite gaskets for metal punching plates for pipe flanges -- Dimensions
GB/T l9675.2-2005 Flexible graphite composite gaskets for metal punch plates for pipe flanges -- Technical specifications
JB/T 87-1994 Asbestos rubber gaskets for pipe flanges
JB/T 88-1994 Metal toothed gaskets for pipe flanges
JB/T 89-1994 Metallic ring gaskets for pipe flanges
JB/T 90-1994 Winding gaskets for pipe flanges
JB/T 6369-2005 Technical specifications for flexible graphite metal wound gaskets
JB/T 6618 2005 Polytetrafluoroethylene tape for metal winding pads - specification
JB/T 8559-1997 Metal covered gasket
JB/T L 0688-2006 Technical specifications for PTFE gaskets
JB/T L 0689-2006 expanded polytetrafluoroethylene sealing tape technical specifications
SH 340111996 Asbestos rubber plate gaskets for pipe flanges
SH 3402 1996 Teflon coated gaskets for pipe flanges
SH 3403-1996 Metal ring pads for pipe flanges
SH 3407-1996 Winding gaskets for pipe flanges
HG/T20592~20635-2009 steel pipe flanges, gaskets, fasteners
GB/T L 047-2005 Pipe element DN(nominal size) definition and selection
GB/T l048 2005 Pipe element PN(nominal pressure) definition and selection
GB/T l2385-2008 Pipe flanges gasket performance test method
GB/T l2621 2008 Pipe flanges gasket stress relaxation test method
GB/T l2622 2008 Pipe flanges -- Test method for compression and resilience of gaskets
GB/T 20671.1-2006 Non-metallic gasket materials classification system and test methods - Part 1: Classification system of non-metallic gasket materials
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification system and test methods - Part 2: Test method for compression rate and resilience of gasket materials
Non-metallic gaskets -- Classification systems and test methods -- Part 3: Test method for liquid resistance of gaskets
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification system and test methods - Part 4: Test method for sealing of gasket materials
Non-metallic gaskets -- Classification systems and test methods -- Part 5: Test method for creep relaxation rate of gaskets
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification systems and test methods - Part 6: Test method for adhesion of gasket materials to metal surfaces
GB/T 20671.7-2006 Non-metallic gaskets materials - Classification system and test methods - Part 7: Test method for tensile strength of non-metallic gaskets
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification systems and test methods - Part 8: Test method for softness of non-metallic gasket materials
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification systems and test methods - Part 9: Test method for durability of cements of cork gasket materials
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification systems and test methods - Part 10: Method for determination of thermal conductivity of gasket materials
Non-metallic gasket materials - Classification systems and test methods - Part 11: Method for determination of mildew resistance of synthetic polymer materials
GB/T 539-2008 oil resistant asbestos rubber sheet
GB/T 540 2008 Test methods for oil-resistant asbestos rubber sheets
GB 912-2008 Carbon structural steel and low alloy structural steel hot rolled sheet and strip
GB/T 3280-2007 Stainless steel cold rolled steel plates and strips
GB/T 3985-2008 asbestos rubber sheet
GB/T 4238-2007 Heat resistant steel sheets and strips
GB/T 5574-2008 Rubber sheet for industrial use
GB/T ll253-2007 carbon structural steel cold rolled sheet and strip
JB/T 6628-2008 Flexible graphite composite reinforced (plate) pad
JB/T 7758.1-2008 Flexible graphite plates -- determination of fluorine content
JB/T 7758.2-2005 Technical specifications for flexible graphite plates
JB/T 7758.3-2005 Flexible graphite plates -- determination of sulfur content
JB/T 7758.4 2008 Flexible graphite plates -- determination of chlorine content
JB/T 7758.5-2008 Flexible graphite plates -- determination of linear expansion coefficient
JB/T 7758.6-2008 Flexible graphite plates -- test method for Shore hardness
JB/T 7758.7-2008 Test method for stress relaxation of flexible graphite plates
JB/T 9141.1-1999 Test method for density of flexible graphite sheets
Fold and edit the installation requirements for this section
Gaskets - Installation requirements for sealing gaskets
1. The sealing surface of the gasket and flange should be cleaned, and there should be no scratches, spots and other defects affecting the sealing performance of the connection.
2, the outer diameter of the sealing gasket should be smaller than the flange sealing surface, the inner diameter of the sealing gasket should be slightly larger than the inner diameter of the pipeline, the difference between the two inner diameters is generally 2 times the thickness of the sealing gasket, in order to ensure that after compression, the inner edge of the sealing gasket will not extend into the container or pipeline, so as not to hinder the flow of fluid in the container or pipeline.
3, sealing gasket preload should not exceed the design provisions, so as to avoid excessive compression of the sealing gasket loss of resilience.
4. When sealing gasket is pressed, it is best to use torque wrench. For large bolts and high strength bolts, it is best to use hydraulic tensioner. The tightening torque should be calculated according to the given sealing gasket compaction, and the oil pressure of the hydraulic tightener should also be determined by calculation.
5. When installing sealing gaskets, tighten the nuts in sequence. But should not screw once to reach the design value. Generally, it should be cycled at least 2~3 times, so that the stress distribution of the sealing gasket is uniform.
6. For pressure vessels and pipelines with inflammable and explosive media, safety tools should be used when replacing sealing gaskets to avoid the collision between tools and flanges or bolts, resulting in sparks and fire or explosion accidents.
7. If there is leakage in the pipeline, the sealing gasket must be replaced or adjusted after pressure reduction treatment. It is strictly prohibited to operate with pressure.
Fold and edit the applicable scope of this paragraph
The choice of gasket material mainly depends on the following three factors: temperature and pressure medium
I. Metal gasket material
1. Carbon steel: recommended maximum operating temperature is not more than 538℃, especially when the medium has oxidation. High quality thin carbon steel plate is also not suitable for the manufacture of inorganic acid, neutral or acidic salt solution equipment, if carbon steel is subjected to stress, used in hot water conditions of equipment accident rate is very high. Carbon steel gaskets are usually used for high concentrations of acid and many alkali solutions. The Brinell hardness is about 120.
2. 304 stainless steel 18-8(chrome 18-20%, nickel 8-10%), the recommended maximum operating temperature is not more than 760℃. In the temperature range of -196~538℃, stress corrosion and grain boundary corrosion are easy to occur. Brinell hardness 160.
3. The carbon content of 304L stainless steel does not exceed 0. 03%. The maximum operating temperature is not more than 760 ° C. Corrosion resistance similar to 304 stainless steel. The low carbon content reduces the precipitation of carbon from the lattice, and the resistance to grain boundary corrosion is higher than that of 304 stainless steel. The Brinell hardness is about 140.
4 316 stainless steel 18-12(chromium 18%, nickel 12%), in 304 stainless steel increase about 2% molybdenum, when the temperature increases its strength and corrosion resistance to improve. When the temperature is increased, it has higher creep resistance than other ordinary stainless steel. The maximum operating temperature is not more than 760 ° C. The Brinell hardness is about 160.
5. The recommended maximum continuous operating temperature of 316L stainless steel is not more than 760℃~815℃. Carbon content is not more than 316 stainless steel has better stress resistance and grain boundary corrosion. The Brinell hardness is about 140.
6. Alloy 20 45% iron, 24% nickel, 20% chromium and a small amount of molybdenum and copper. The recommended maximum operating temperature ranges from 760 ° C to 815 ° C. Especially suitable for manufacturing sulfuric acid corrosion resistant equipment, Brinell hardness of about 160.
7. Aluminum aluminum (content not less than 99%). Aluminum has excellent corrosion resistance and machining properties, suitable for the manufacture of double clamp gaskets. Brinell hardness is about 35. The maximum continuous operating temperature is not more than 426 ° C.
8. Copper Copper is similar in composition to pure copper and contains trace amounts of silver to increase its continuous operating temperature. The maximum continuous operating temperature is recommended to be less than 260 ° C. Brinell hardness is about 80.
9. Brass (copper 66%, zinc 34%), in most working conditions, has good corrosion resistance, but not suitable for acetic acid, ammonia, salt and acetylene. The maximum continuous operating temperature is recommended to be less than 260 ° C. The Brinell hardness is about 58.
10. Hastelloy B-2 (26-30% molybdenum, 62% nickel and 4-6% iron). The maximum operating temperature does not exceed 1093 ° C. It has excellent corrosion performance of hydrochloric acid in heat resistant concentration. It also has excellent resistance to the corrosion of wet hydrogen chloride gas, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid and reducing salt solution. High strength under high temperature conditions. The Brinell hardness is about 230.
11. Hastelloy C-276 16-18% molybdenum, 13-17.5% chromium, 3.7-5.3% tungsten, 4.5-7% iron, the rest are nickel). The maximum operating temperature does not exceed 1093 ° C. Excellent corrosion resistance. It has excellent corrosion resistance to all kinds of cold nitric acid or boiling nitric acid with a concentration of 70%. It has good corrosion resistance to hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid and excellent stress corrosion resistance. The Brinell hardness is about 210.
12. Incornel 600 nickel base alloy (77% nickel, 15% chromium and 7% iron). The maximum operating temperature does not exceed 1093 ° C. High strength under high temperature conditions, commonly used to solve the problem of stress corrosion equipment. At low temperature, it has excellent co-processing performance. Brinell hardness is about 150.
A gasket is











Update time: